At Studio, we believe that the success of any mobile application hinges on its ability to meet and exceed user expectations. By prioritizing the needs, preferences, and behaviors of users, we build products that are intuitive, engaging, and foster engagement. So what makes User-centered design (UCD) different from standard design processes?
Understanding User-Centered Design
User-centered design is an iterative design process that places the user at the center of each stage of development. It involves understanding the user's needs and designing products that provide meaningful and relevant experiences. This approach contrasts with traditional design methodologies, which often prioritize technical or business requirements over the end-user experience.
Our designers put themselves in the user's shoes, considering their challenges, goals, and motivations. This empathetic approach ensures that the end product resonates with users, leading to higher satisfaction and participation.
1. User Research
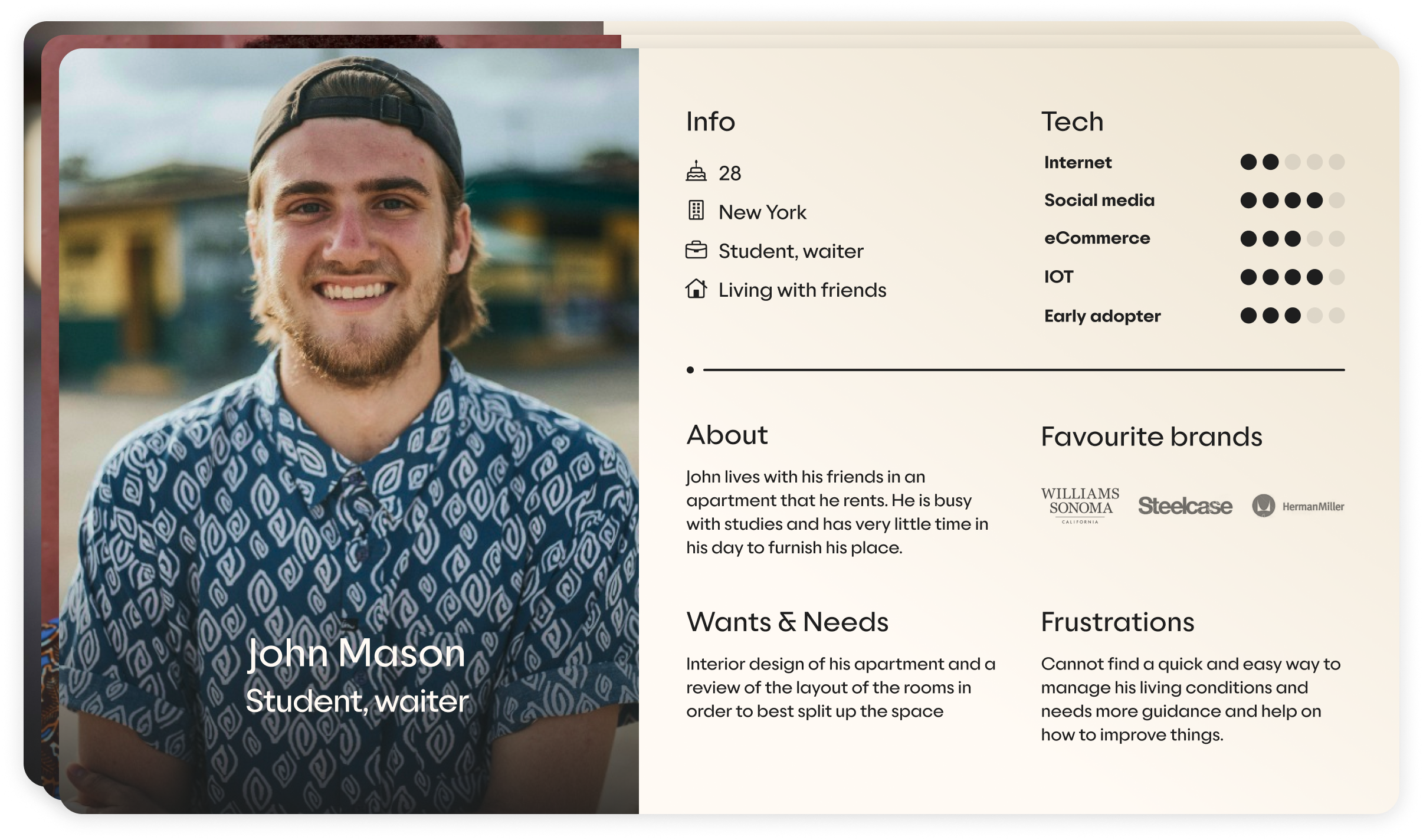
Understanding our target audience is the first step in our user-centered design process. Conducting thorough user research helps us identify the characteristics, behaviors, and needs of potential users. Methods such as surveys, interviews, and focus groups provide valuable insights into user preferences and pain points.
2. Usability and Accessibility
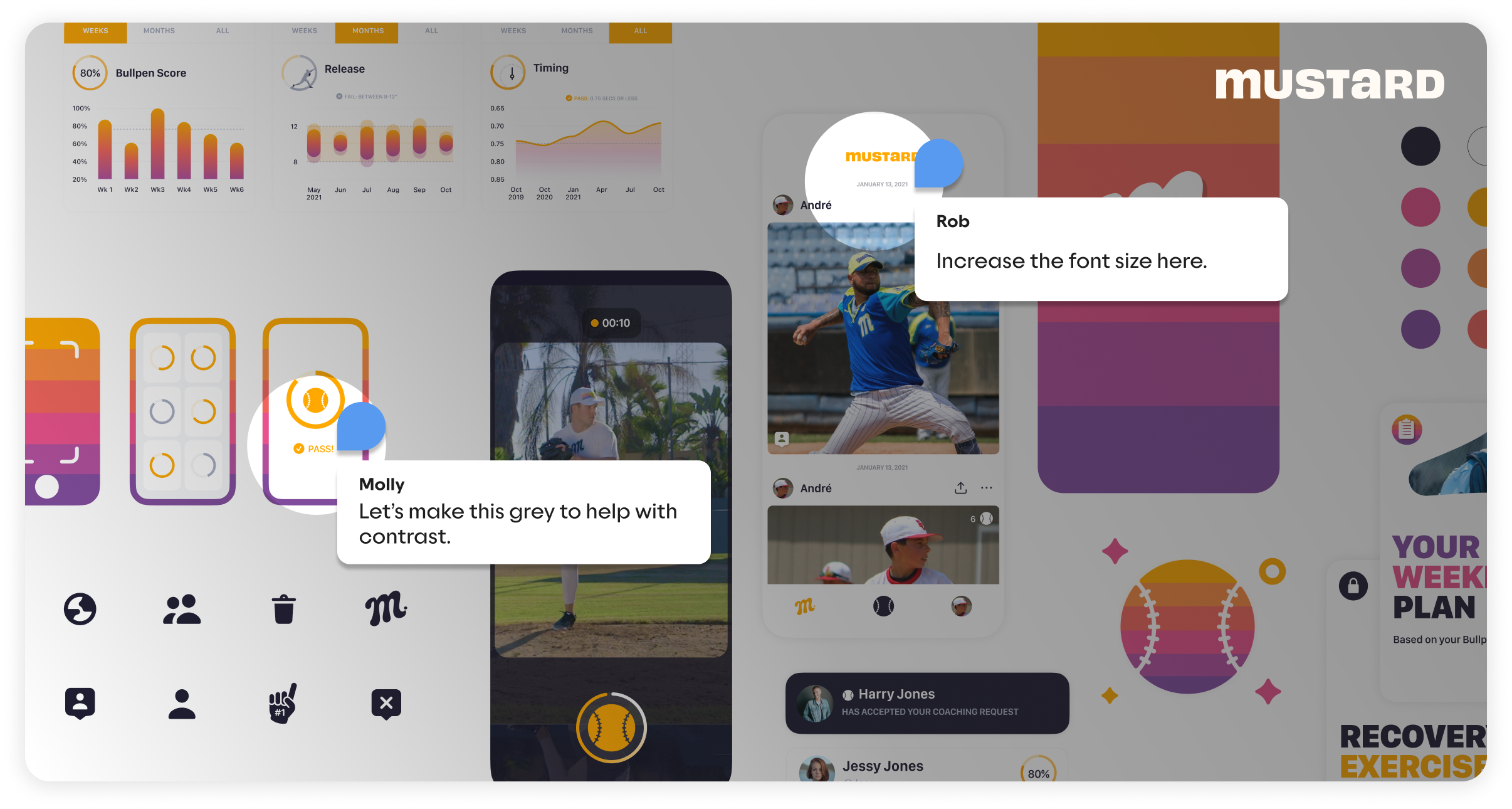
Usability is a critical component of user-centric design. A mobile application must be easy to use, with a clear and intuitive interface that minimizes the learning curve. Key usability principles include:
- Consistency: Ensuring a consistent layout, design elements, and interactions across the application to prevent user confusion.
- Feedback: Providing immediate and clear feedback for user actions, such as button presses or form submissions.
- Efficiency: Designing workflows that minimize the number of steps required to complete a task.
Accessibility is equally important, ensuring that the application can be used by as many people as possible, including those with disabilities. Adhering to accessibility standards, such as the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG), ensures that our app is inclusive. This includes providing text alternatives for non-text content, ensuring sufficient color contrast, and designing for screen reader compatibility.
View the Mustard case study
3. Intuitive Navigation
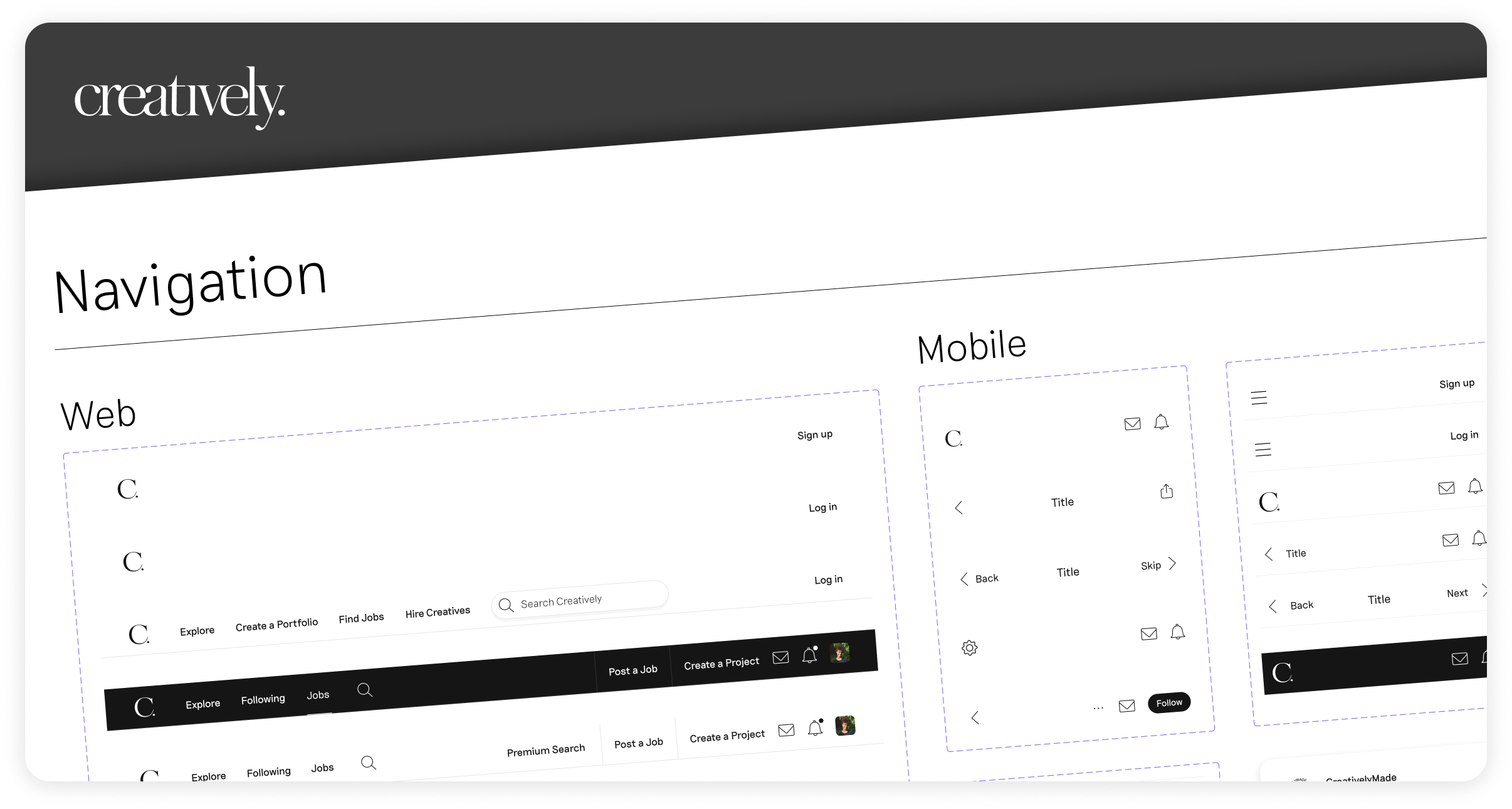
Navigation is a crucial aspect of mobile design, significantly impacting user experience. Users should be able to find what they need quickly and easily, without getting lost in a maze of screens. Best practices for intuitive navigation include:
- Clear Hierarchy: Organizing content in a logical structure, with the most important information easily accessible.
- Standard Navigation Patterns: Using familiar navigation patterns, such as bottom navigation bars or hamburger menus, helps users navigate effortlessly.
- Search Functionality: Including a robust search feature that allows users to quickly find specific content or features.
View the Creatively case study
4. Aesthetic and Minimalist Design

Aesthetics play a significant role in user experience. A visually appealing design not only attracts users but also enhances their overall satisfaction. However, aesthetics should not compromise functionality. Minimalist design, which focuses on simplicity and clarity, is often more effective in mobile applications. Key principles of minimalist design include:
- Focus on Content: Prioritizing content over decorative elements ensures that users can easily access the information they need.
- Whitespace: Using ample whitespace to create a clean and uncluttered interface.
- Consistent Visual Style: Maintaining a consistent visual style throughout the app, including colors, fonts, and iconography.
5. Performance and Responsiveness
Performance is a critical factor in user satisfaction. Mobile applications must load quickly and respond efficiently to user inputs. There are a number of areas design can help with this:
- Optimizing Load Times: Minimizing the size of assets and using efficient coding practices to reduce load times.
- Responsive Design: Ensuring that the application performs well across different devices and screen sizes.
- Mobile + Desktop Assets: Providing mobile-optimized and desktop-optimized assets for loading on each device type.
- Regular Testing: Continuously testing the app for performance issues and proactively optimizing.
6. User Feedback and Iterative Design
The process of designing around users is ever evolving. So constantly collecting user feedback is essential for understanding how users interact with the app and identifying areas for improvement. Some of the methods we use to gather this data are:
- In-App Surveys: Prompting users to provide feedback through short surveys within the app.
- Analytics: Using analytics tools to track user behavior and identify pain points or drop-off areas.
- User Testing: Conducting regular user testing sessions to observe how real users interact with the app and gather qualitative insights.
An iterative design process, where the app is continuously refined based on user feedback, ensures that the final product meets users' needs and expectations. This approach allows us to make incremental improvements and address issues before they become major problems.
Conclusion
User-centered design is essential for creating a successful mobile application. Prioritizing the needs and preferences of users enables us to build experiences that are not only functional but also enjoyable and memorable. Through thorough user research, intuitive navigation, aesthetic and minimalist design, and a commitment to usability and accessibility, we create mobile apps that truly resonate with their audience.
Continuous user feedback and an iterative design process further ensure that our apps evolve to meet changing user needs and preferences, leading to sustained success in the competitive mobile landscape.
Designing a product? Let our experts help. Contact Studio today.